In Cities: Skylines II, zones will play a much more important role than in the previous installment of the game. In addition, the game will feature distinctive buildings that are a combination of unique and zoned buildings.
Zoning Tools
Zoning tools offer several familiar options, such as Fill, Select and Paint. The Fill tool automatically fills the selected zone cells with the selected zone type. The Selection tool allows you to select rectangular areas of any size and fill them with the selected zone type. The Paint tool allows you to create zones with precision, allowing you to paint one cell at a time. Now you can also choose the zone type and preferred tool mode when creating a zone.
Simplifying de-zoning
Deleting zones has been simplified. Now you don’t need to use a separate tool to delete zones. Just press the right mouse button while any zone tool is active. For example, using the Fill tool, you can delete the entire continuous area of a zone. The Selection tool allows you to designate a rectangular area for deletion, and the Paint tool allows you to delete zones cell by cell. Changing the zone type is also now easier and faster, not requiring you to detach the zone from the previous type before adding a new one.
Architectural themes
A new feature is the ability to zone buildings with different architectural motifs using city planning tools. When setting up a new city, you can choose an architectural theme that will affect the appearance of buildings, street signage, roadside fixtures and official vehicles. Urban planning tools allow you to zone buildings in both North American and European styles, giving you the ability to mix the two styles in one city. For example, a European city can have North American-style buildings, and vice versa.

Zone types
Cities: Skylines II introduces a greater variety of residential zone types compared to the previous version of the game, allowing the creation of more diverse and realistic cities. In addition to well-known zones, such as low-density development with single-family homes and high-density development with high-rise residential buildings, new types of residential zones have been introduced.
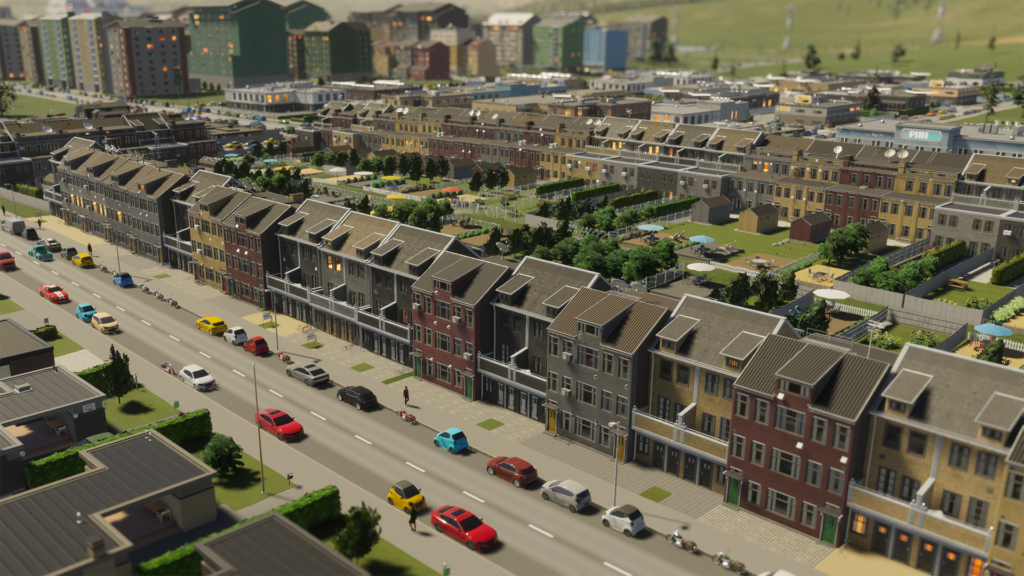

These include medium-density row development, where houses are adjacent to each other, medium-density development with apartment buildings, mixed-use development, where stores occupy the first floor of buildings and apartments are above, and low-rent housing with large apartment buildings, which are ideal for low-income residents such as students and young adults leaving their parents’ home to live in their own first apartment. Medium-density row developments are narrow buildings with larger apartments but higher maintenance costs. High-density developments, on the other hand, accommodate more people in less space, offering cheaper rents through cost sharing.
Mixed-use development creates more realistic cities where residential and commercial zones coexist. This solution addresses the needs of these two types of zones, allowing them to share valuable space in busy city centers. Commercial companies support the economic viability of mixed housing, leading to lower rents for residents.
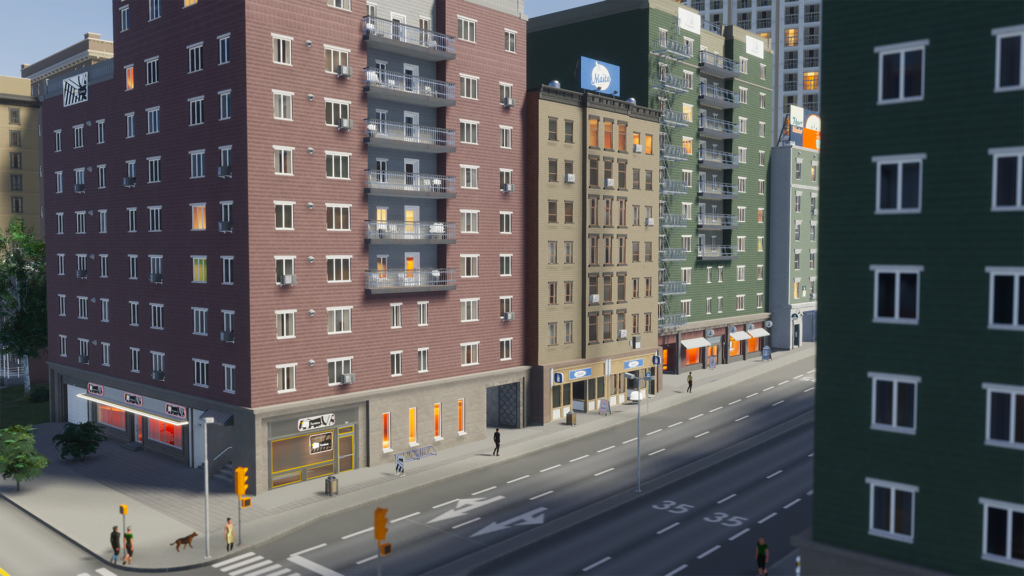

Commercial zones
Commercial zones are places where different types of buildings are located, offering a variety of products – both locally made and imported from outside. Commercial zones often develop near residential areas, thus attracting customers.
Low-density businesses tend to be boutiques, gas stations, small stores and bars, while high-density businesses include supermarkets, department stores and entertainment venues such as theaters and hotels. Smaller companies tend to have fewer employees and serve fewer customers, while larger companies have more employees and serve more people. This means that larger companies can sell more goods from their inventory compared to smaller, low-density companies.
Businesses benefit from local production, which allows them quick access to goods. Local manufacturers also benefit from nearby retailers, which reduces the cost of transporting manufactured goods to retail stores and increases profits per unit of goods sold.

Industrial zones
Industrial zones consist of factories and warehouses, where factories and workshops are predominant, but warehouses can also be found, used by companies to store finished goods awaiting transport or buyers.
Industrial zones produce various types of products, which are either transported from external sources via delivery trucks or are extracted and processed on-site in specialized industrial areas. Some of these products go directly to commercial enterprises that sell them to customers (e.g., food), while others are initially supplied to commercial enterprises, where they are further processed into products or intangible goods.
Industrial zones usually try to sell their products to local buyers, which is more profitable due to lower transportation costs. If there is an overproduction of a particular product, companies can export the surplus to other cities, but this is less economically advantageous due to higher transportation costs. Companies regularly analyze their operations and adjust the number of employees according to current market needs and changes in the market.

Office zones
Office zones, like commercial zones, consist of offices of varying densities, including both smaller office buildings and imposing office towers with distinctive glass facades. Intangible goods and services are generated in these areas, which target both citizens and companies. Office companies are engaged in transforming technological products generated in industrial zones into software and other intangible goods, such as telecommunications, finance and media.
Companies operating in office zones include banks, electronics retailers, law firms, insurance companies and telecommunications providers. Software plays a key role as the basic material for the production of various intangible goods, although it is not itself available to individual customers. Other products and services, such as telecommunications and finance, have a much broader range of applications, as private customers also use them. Media, on the other hand, are delivered directly to citizens in the form of electronic equipment, video games and other related products.

Suitability of the zone
Each zone type has an informative view available when creating zones. This view contains relevant information about the relevant areas for a given zone category. For example, in the case of commercial zones, information about potential customers in a given location is available, and for residential zones information about the level of land contamination is visible, making it easier to avoid such areas during urban planning. The information view also indicates areas that may be less suitable due to high land values, which affect rents for low-density housing.
Demand for zones
Urban development is based on different types of zones, which influence each other. The arrival of new residents increases the demand for housing, which stimulates the development of industry and commerce, creating demand for jobs and recreational space. Industrial development, in turn, generates demand for commercial space to sell manufactured goods. The creation of new businesses creates jobs and increases demand for housing.
Adjusting the level of taxes according to the level of education and the type of products and goods can affect local demand. Taxes can be used to promote specific products and industries or to support developing sectors of the economy.

Housing demand
Demand for housing is increasing due to a variety of factors, including the arrival of new residents who are looking for work, studying or wishing to settle in an attractive city. Families and the elderly often prefer larger apartments, which increases the demand for lower- and medium-density housing. Single-person households and students, on the other hand, are more likely to choose smaller apartments, such as medium-density buildings and high-density residential towers, attracted by their lower cost of living.
In residential areas, demand for housing is also growing along with the availability of jobs in the industrial, retail and office sectors. The arrival of new workers generates demand for adequate housing. However, when unemployment and job shortages increase, demand for housing may decline until these problems are resolved. The situation can be complicated when there are many built but unoccupied houses in a city, limiting demand for housing until the available properties are fully utilized.

Commercial demand
Demand in commercial zones is based on producers who create goods for sale, the availability of potential customers and the employment needs of the local community. Industrial zones produce goods that must find buyers to generate profits. They usually prefer to sell in the local market, which increases the demand for local commercial enterprises.
Just having goods and products to sell is only part of the success. Commercial zones also need sufficient purchasing power from local residents to not only survive, but also to prosper. In this regard, local demand for goods and products plays an important role in creating demand for commercial services. Residents want to purchase items for their households, but also use shopping as a leisure activity.
Commercial demand can also increase if companies notice the availability of adequate labor in the city. When companies have enough workers to fill their positions, they can increase their profitability.

Industrial demand
Industrial demand is driven by the needs of citizens seeking employment in the manufacturing sector, as well as local trading companies that need a supply of goods and products to sell. In addition, the availability of local sources of raw materials, used by specialized industries, can further increase this demand. The establishment of special industrial areas allows access to raw materials locally, which helps reduce transportation costs and increases profits.
A key component of industrial demand is the availability of a skilled labor force. The arrival of new residents to the city directly affects the demand for workers in various sectors, including industrial zones. Companies are always looking to optimize their production and are seeking skilled workers. As companies grow, their workforce requirements increase, targeting workers with higher education. This translates into increased productivity and efficiency, which increases profits.
Warehouses also play an important role in the production process, allowing companies to store manufactured goods and products. Companies, usually with relatively small warehouses, try to sell their products as quickly as possible. However, the presence of local warehouses provides greater flexibility and gives time to find suitable buyers, which is beneficial in the absence of current demand, while allowing for continuity in production.

Demand for offices
Demand for offices is growing mainly due to citizens who are looking for jobs in the office sector, and companies and individuals who need various intangible services provided by offices. Software developed in office zones is used in the manufacturing industry as well as in other office businesses. As new software is developed, the need for offices to continue developing and using it also increases.
A key element of demand in office zones is the availability of appropriately skilled workers, which translates into higher productivity and efficiency for companies. As with other industries, the better matched employees are to the needs of companies, the higher profits they generate. The type of intangible services preferred by customers may depend on age group. Adults and seniors may focus more on financial services offered by the banking sector, while children and teenagers may use media products more often.
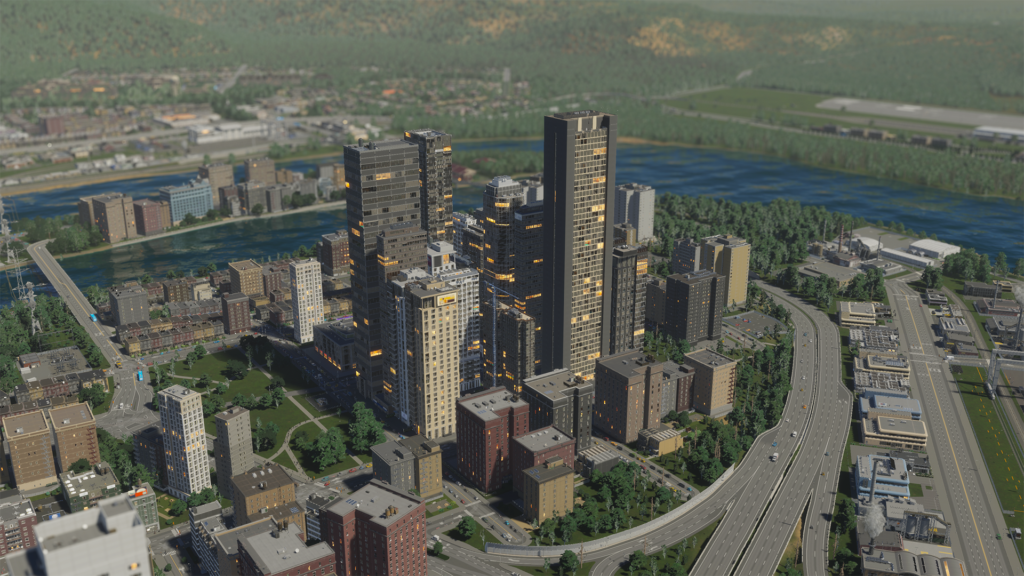

Specialization of the city
Companies that operate in industries that use the same materials and produce similar goods benefit from geographic proximity. These industries and offices are often concentrated in neighborhoods where similar businesses already exist. This allows them to network, share experiences and more easily attract highly skilled workers, which increases overall productivity. As the number of companies producing similar products or goods increases, a city-wide specialization is created, resulting in higher profits and overall development. Fostering city-wide specialization can be achieved by creating dedicated industrial areas that provide the materials necessary for companies that benefit from city-wide specialization. In addition, adjusting the tax system to promote these products and goods can further support the development of these industries.
Land value and building levels
Land value is a key factor that influences the attractiveness of various locations for both citizens and businesses. The main factors driving land value include access to large homes, proximity to stores, services, schools, jobs and a clean environment. When residents find suitable homes that meet their needs and are able to pay higher rents, the area becomes more attractive and appreciates in value. However, simply providing public services does not always translate into increased land values. The key is to meet the needs of both residents and businesses, both in terms of services and product availability, making the area valuable for their operation.
High demand for specific types of residential zones can lead to increases in rents and land values, as more people want to live there than there is housing available. To control the increase in land values, different property taxes can be adjusted, which can encourage or discourage citizens from settling in an area. Creating different types of zones with varying demand can also help keep land values under control when demand drops.
The value of land also affects companies, which choose locations based on production and transportation costs. Companies incur transportation costs for both raw materials and finished products. The lower these costs are, the more attractive a location is. For companies, surplus funds are often invested in building improvements, helping to bring them to a higher level. This is why it is so important to maintain an adequate level of service availability and infrastructure efficiency for both residents and businesses.
Levels of construction
There are five levels from 1 to 5 in the building zone, which reflect the quality of the buildings and the wealth of the residents. As the level of a building increases, so does its standard of maintenance, which results in higher rent.
For residential buildings, a higher level means less household electricity and water consumption. Levels 3 and 5 also offer more housing in higher-density buildings.
Commercial buildings see a decrease in electricity and water consumption per unit of goods or services sold. Companies with higher building levels are able to produce faster and can offer their products and services at lower prices, thus attracting customers.
Similar changes are taking place in manufacturing and office buildings, where lower electricity and water consumption per unit of goods goes hand in hand with higher building levels, which means more efficient production processes and reduced waste and pollution.
Every other level of the buildings brings visual changes, reflecting an increase in quality. Lower levels present a more streamlined look, while higher levels feature more modern and detailed finishes.
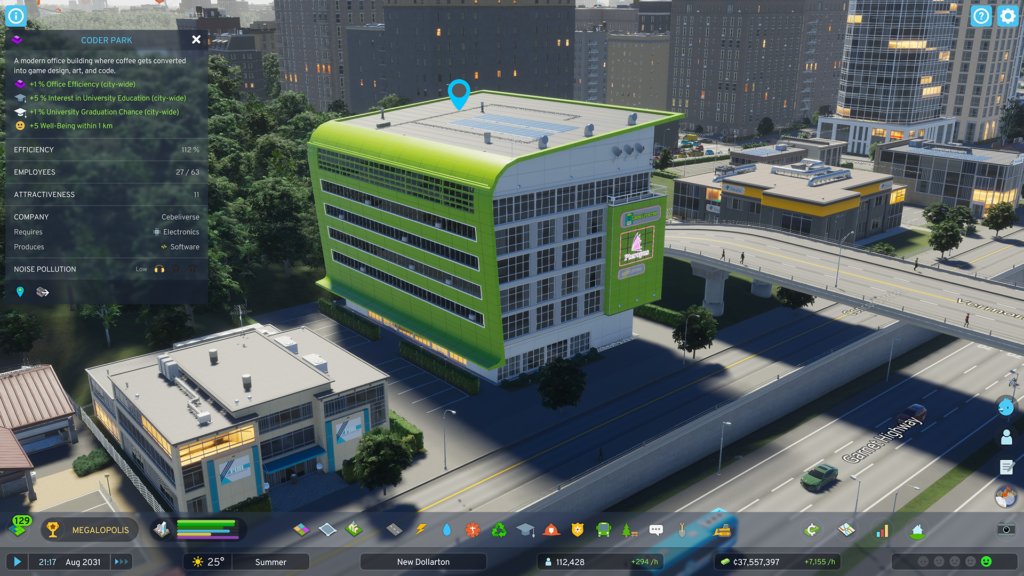
Signature buildings
Cities: Skylines II features distinctive buildings that can be described as unique, relocatable zoned buildings. They fall into residential, commercial, industrial and office categories. Each of these buildings has its own criteria for unlocking, such as reaching a specific milestone of progress, achieving a certain level of citizen satisfaction, and having a certain number of cells in low-density zones. Once these conditions are met, the buildings become available and can be placed on the map, just like service buildings. Each of these buildings is unique and can be built only once, but there is no cost involved. It is also possible to move and demolish them, allowing them to be built again in the future.
Residential buildings vary in size, comprising residences, medium-density buildings and high-rise residential buildings. They function on a zoning basis and affect the economic cycle associated with the zone. Residential buildings attract new residents, while commercial buildings, office buildings and factories seek suitable businesses to occupy them. Businesses in signature buildings are subject to the same laws of success and risk as other businesses, competing for employees, customers and making a profit.
Distinctive buildings allow the erection of large commercial buildings, huge factories or impressive offices that function on a zoned building basis.
Each signature building is attributed with one or more positive effects that affect both the surrounding area and the city as a whole. Some of these effects relate to the well-being of the residents and the tourist appeal of the city, while others increase the productivity of industry or education at a higher level. Distinctive buildings introduce fascinating new possibilities and effects for your city.
Sources:
https://www.paradoxinteractive.com/games/cities-skylines-ii/features/zones-signature-buildings

